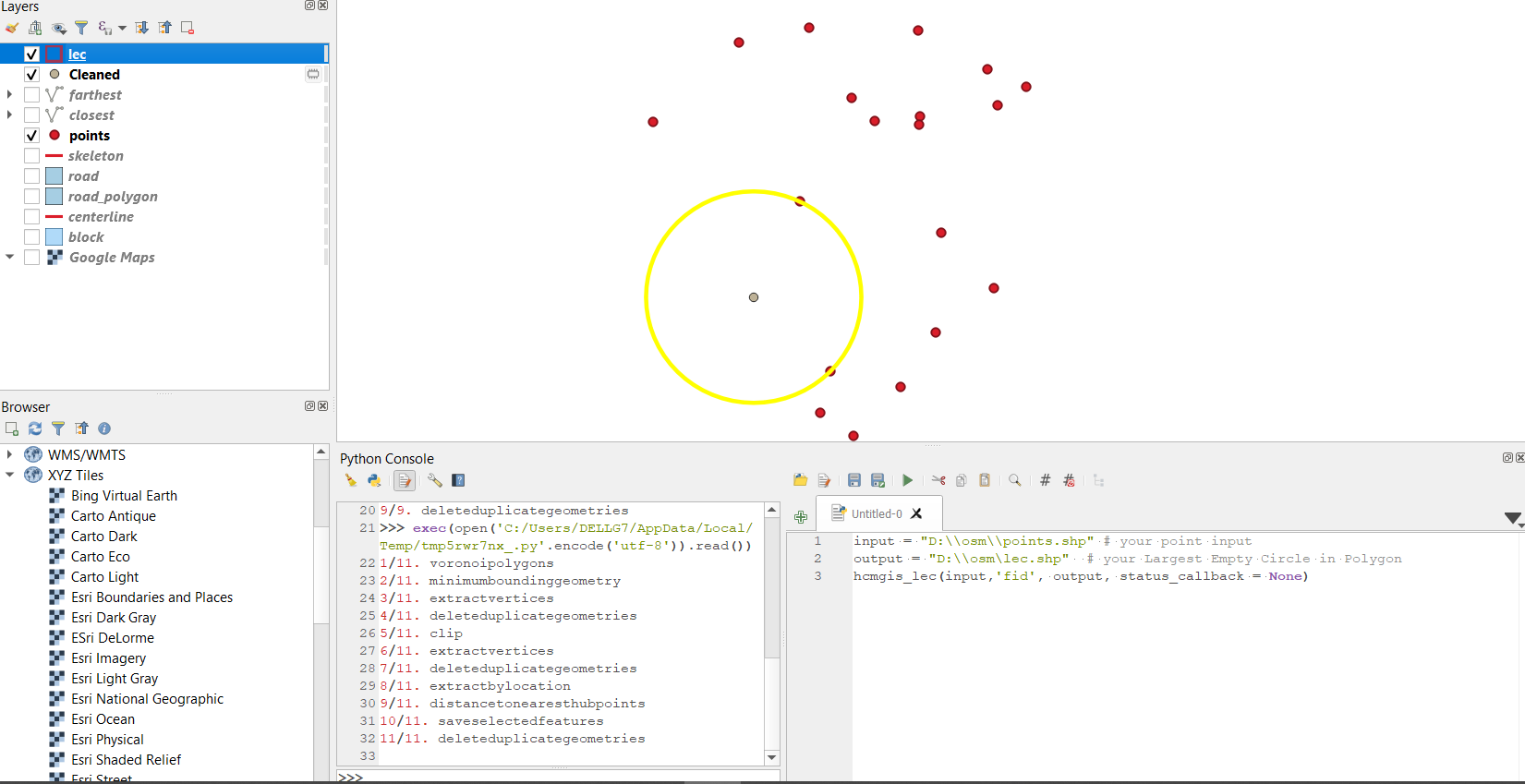
Call HCMGIS Library in QGIS Python Console
1. Import HCMGIS library:
After install HCMGIS Plugin, open QGIS Python Console and import HCMGIS.hcmgis_library:
from HCMGIS.hcmgis_library import *
2. List of HCMGIS Library Functions:
hcmgis_basemap_load()
hcmgis_covid19()
hcmgis_covid19_timeseries()
hcmgis_covid19_vietnam()
hcmgis_medialaxis(layer, field, density,output,status_callback = None)
hcmgis_centerline(layer,density,chksurround,distance,output,status_callback = None)
hcmgis_closest_farthest(layer,field,closest,farthest,status_callback = None)
hcmgis_lec(layer,field,output,status_callback = None)
3. Call HCMGIS Library:
Add dozens of basemaps to XYZ Tiles of QGIS:
hcmgis_basemap_load()
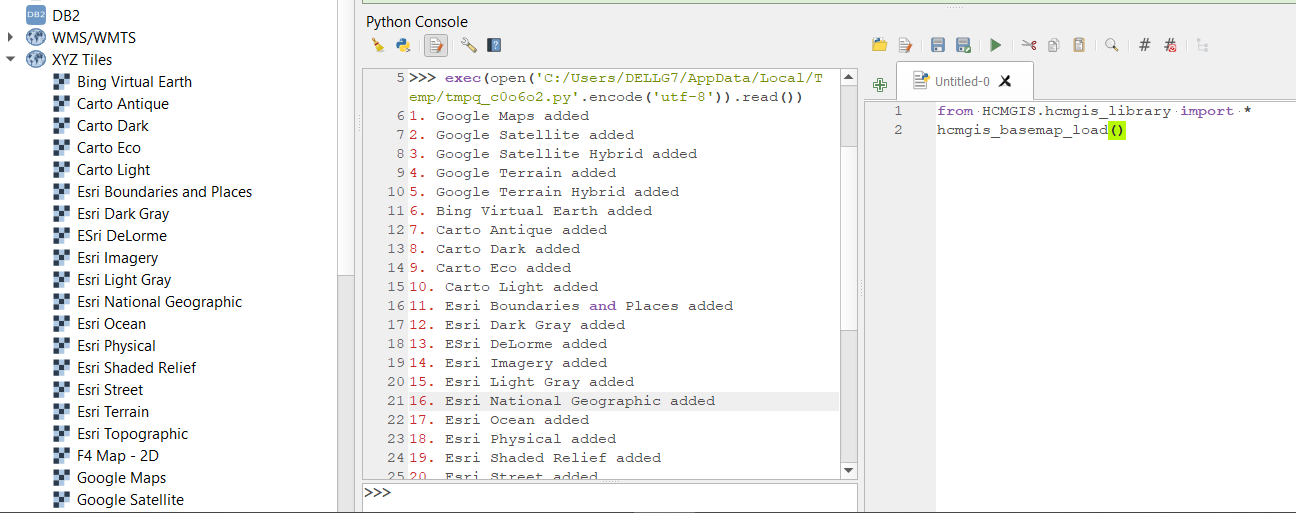
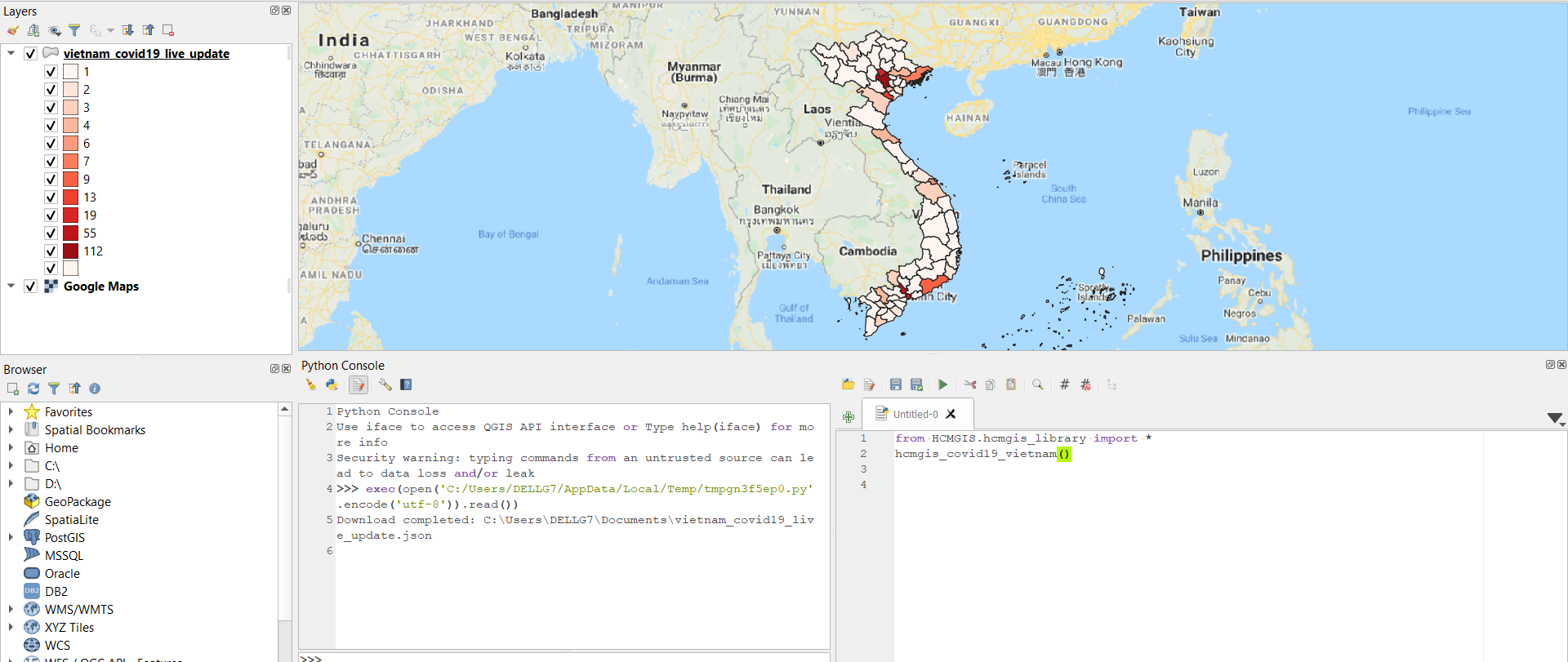
Download Global COVID-19 live update Data
hcmgis_covid19()
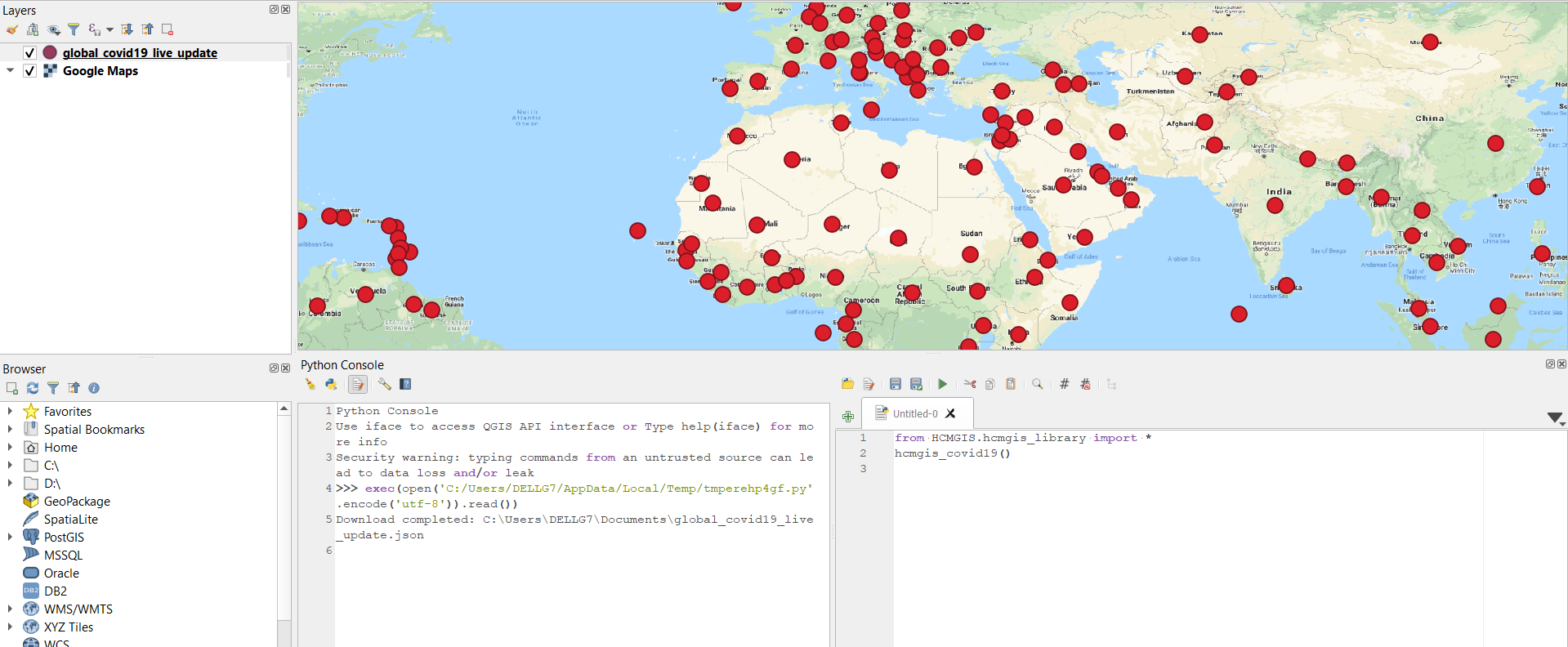
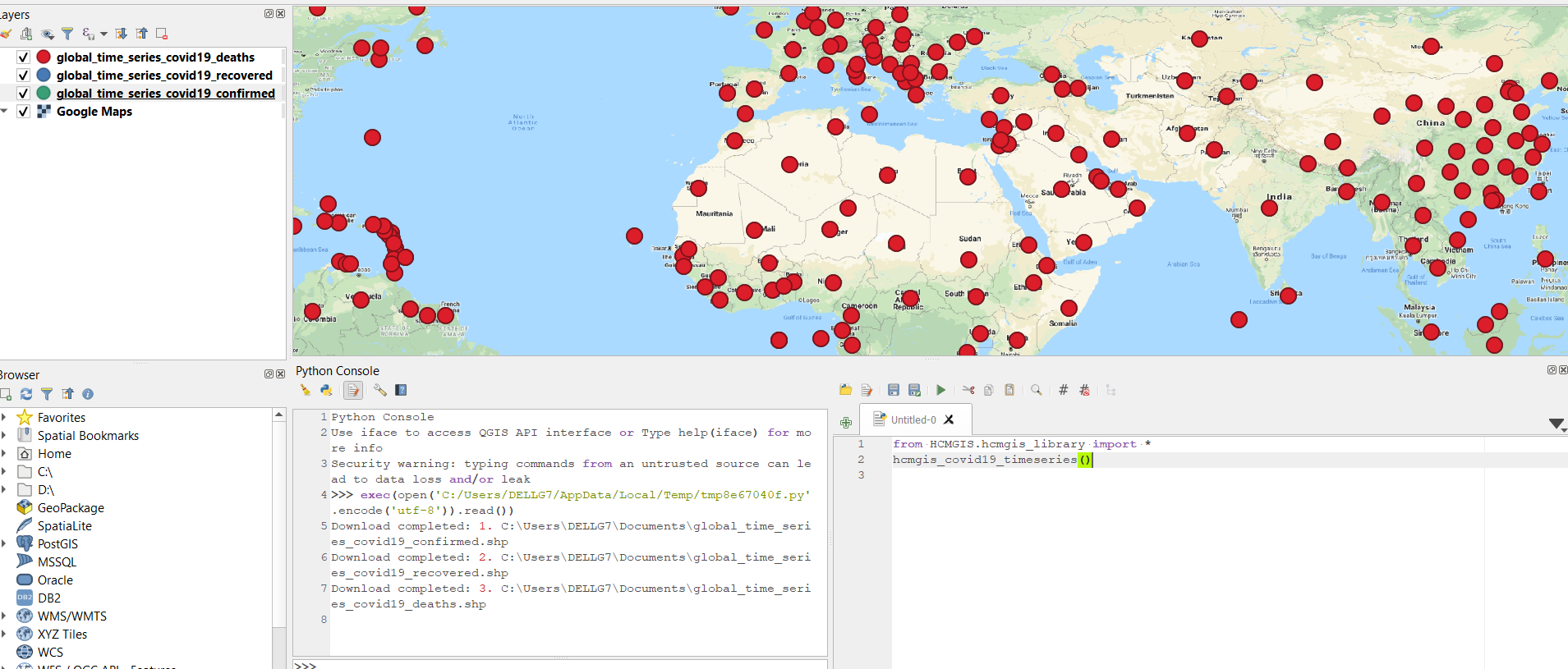
Download Global COVID-19 Timeseries Data
hcmgis_covid19_timeseries()
Download Vietnam COVID-19 live update in Polygon
hcmgis_covid19_vietnam()
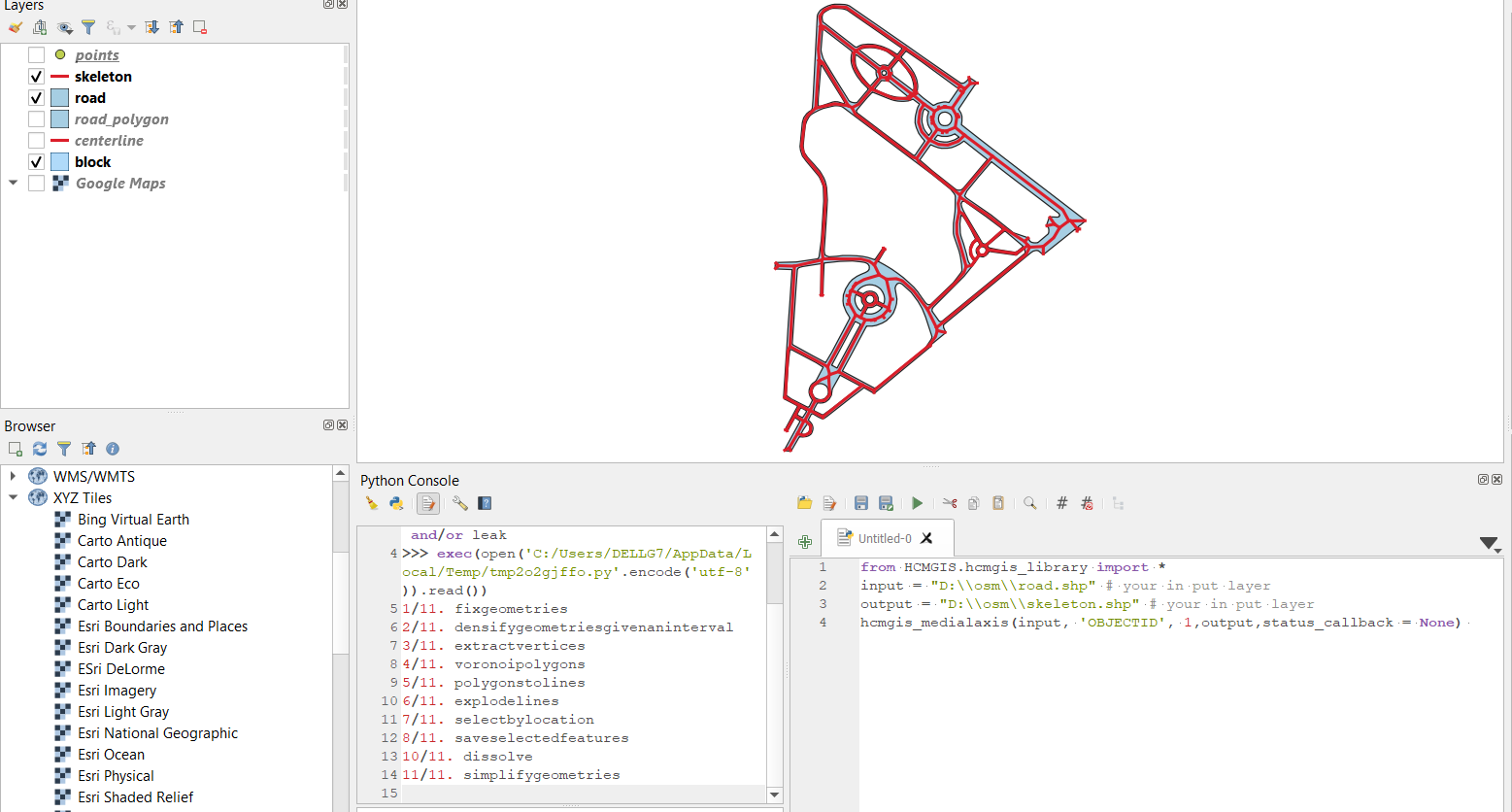
Create Medial Axis/ Skeleton from Road in Polygon
hcmgis_medialaxis(layer, field, density,output,status_callback = None)
PLEASE DON’T MIND the parameter ‘status_callback = None’ in these functions below
because it is written for HCMGIS Plugin with GUI interaction and also for running in Python console
input = "D:\\osm\\road.shp" # your polygon input layer
output = "D:\\osm\\skeleton.shp" # your skeleton output in .sqlite, .shp, .geojson, .gpkg or kml
hcmgis_medialaxis(input, 'OBJECTID', 1,output,status_callback = None)
# hcmgis_medialaxis(layer, field, density,output,status_callback = None)
# layer: input layer
# field: unique field of input layer, in this case is 'OBJECTID'
# density (float value): densify geometries with a given interval (in this case is 1 meter).
# Smaller density value returns smoother centerline but slower
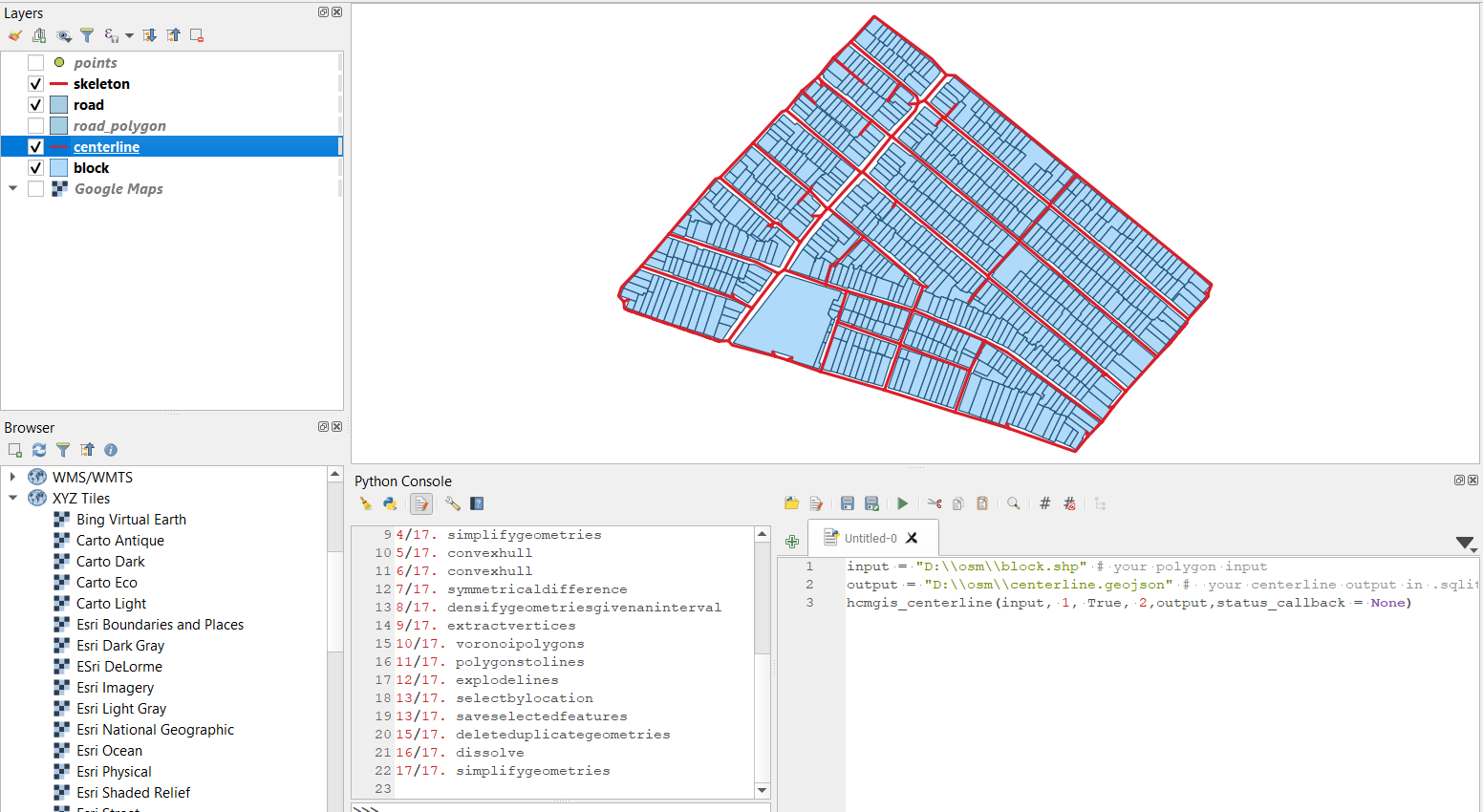
Create Centerline from Building block
hcmgis_centerline(layer,density,chksurround,distance,output,status_callback = None)
input = "D:\\osm\\block.shp" # your polygon input
output = "D:\\osm\\centerline.geojson" # your centerline output in .sqlite, .shp, .geojson, .gpkg or kml
hcmgis_centerline(input, 1, True, 2,output,status_callback = None)
# hcmgis_centerline(layer,density,chksurround,distance,output,status_callback = None)
# density (float value): densify geometries with given an interval (in this case is 1 meter).
# Smaller density value returns smoother centerline but slower
# chksurround: if chksurround is True, then the function will also create a surrounding 'centerline'
# with a given "distance" to the bounding box of building block (in this case is 2 meters)
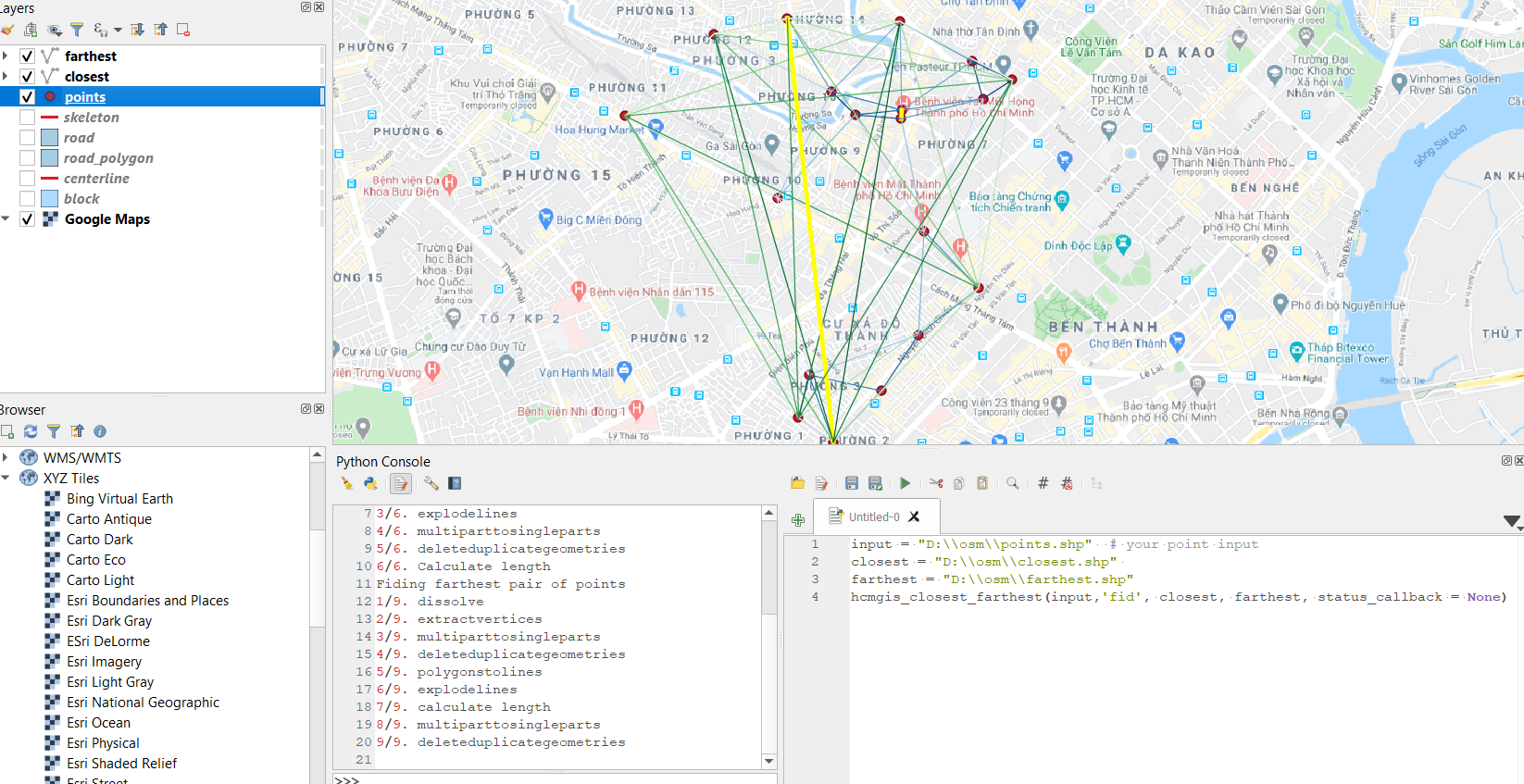
Closest/ farthest pair of points
hcmgis_closest_farthest(layer,field,closest,farthest,status_callback = None)
input = "D:\\osm\\points.shp" # your point input
closest = "D:\\osm\\closest.shp" # your closest pair of point output in polyline
#connecting closest, second closest,.. pairs of points with distance attribute.
farthest = "D:\\osm\\farthest.shp" # your farthest pair of point output in polyline
#connecting farthest, second farthest,.. pairs of points with distance attribute.
hcmgis_closest_farthest(input,'fid', closest, farthest, status_callback = None)
# hcmgis_closest_farthest(layer,field,closest,farthest,status_callback = None):
# "field": the unique field of input layer, in this case is 'fid'
Largest Empty Circle
hcmgis_lec(layer,field,output,status_callback = None)
input = "D:\\osm\\points.shp" # your point input
output = "D:\\osm\\lec.shp" # your Largest Empty Circle in Polygon
hcmgis_lec(input,'fid', output, status_callback = None)
# hcmgis_lec(layer,field,output,status_callback = None):
# "field": the unique field of input layer, in this case is 'fid'